According to allcitycodes, Djibouti is a small country located in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Eritrea, Ethiopia and Somalia. It has a hot semi-arid climate with very little rainfall and high temperatures throughout the year. The average temperature across the year is around 28°C (82°F). Summer months (June to August) are generally the hottest, with temperatures reaching up to 40°C (104°F). Winters (December to February) are typically milder, with temperatures ranging from 18-28°C (64-82°F). Rainfall is scarce in Djibouti, averaging between 100-200 millimeters (4-8 inches) per year. Most of the rain falls during summer months as a result of monsoon winds coming from the Indian Ocean. The rest of the year is usually dry and hot. In addition to its hot climate, Djibouti is also prone to several natural hazards including floods, landslides and earthquakes. These events can cause significant damage to infrastructure and loss of life when they occur; for example in 2019 heavy rains caused extensive flooding across parts of Djibouti leading to several deaths. In addition to natural hazards, Djibouti is also vulnerable to extreme weather events such as storms which can cause significant damage if they reach the country’s shores. It is important for people living in Djibouti to be prepared for these events by having an emergency plan in place and stocking up on essential supplies such as food and water before any storm arrives. Check eningbo for Djibouti in 2012.
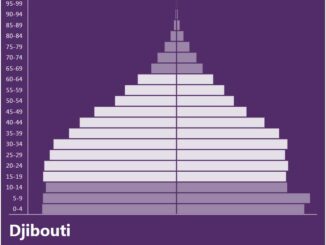
Djibouti 2000
Yearbook 2000 Djibouti. In February, the government signed a peace agreement with a radical faction of the militant opposition group FRUD (Front pour la Restoration […]